
For example, analysts can calculate the margin per unit sold and use forecast estimates for the upcoming year to calculate the forecasted profit of the company. Increase revenue by selling more units, raising product prices, shrinking product size while keeping the same cost, or focusing on selling products with high margins. Investors often look at contribution margin as part of financial analysis to evaluate the company’s health and velocity.
Contribution Margin vs. Gross Profit Margin
Say a machine for manufacturing ink pens comes at a cost of $10,000. The contribution margin helps you understand how much money a product, department, or an entire company is contributing to overheads and profit, and helps in decision-making about pricing, product volumes, sales strategies, etc. Calculate contribution margin for the overall business, for each product, and as a contribution margin ratio. Calculations with given assumptions follow in the Examples of Contribution Margin section.
Products
Each profit measure can be expressed as total dollars or as a ratio that is a percentage of the total amount of revenue. Typical variable costs include direct material costs, production labor costs, shipping supplies, and sales commissions. Fixed costs include periodic fixed expenses for facilities rent, equipment leases, insurance, utilities, general & administrative (G&A) expenses, research & development (R&D), and depreciation of equipment.
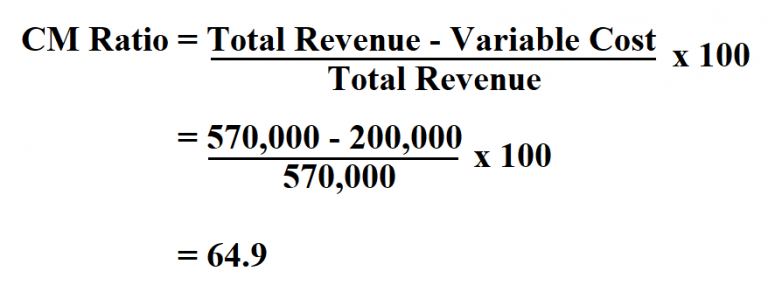
Is a high contribution margin ratio good?
To calculate the contribution margin, we must deduct the variable cost per unit from the price per unit. While there are plenty of profitability metrics—ranging from the gross margin down to the net profit margin—the contribution margin metric stands out for the analysis of a specific product or service. The contribution margin (CM) is the profit generated once variable costs have been deducted from revenue.
- Instead, management uses this calculation to help improve internal procedures in the production process.
- The more it produces in a given month, the more raw materials it requires.
- Along with managing the purchasing process, inventory is maintained by sensors that let managers know when they need to restock an item.
- This is information that can’t be gleaned from the regular income statements that an accountant routinely draws up each period.
- The ratio can help businesses choose a pricing strategy that makes sure sales cover variable costs, with enough left over to contribute to both fixed expenses and profits.
To illustrate how this form of income statement can be used, contribution margin income statements for Hicks Manufacturing are shown for the months of April and May. A university van will hold eight passengers, at a cost of \(\$200\) per van. If they send one to eight participants, the fixed cost for the van would be \(\$200\). If they send nine to sixteen students, the fixed cost would be \(\$400\) because they will need two vans.
How to Conduct an Accounts Payable Audit: What You Should Know
For example, if the cost of raw materials for your business suddenly becomes pricey, then your input price will vary, and this modified input price will count as a variable cost. In the same example, CMR per unit is $100-$40/$100, which is equal to 0.60 or 60%. So, 60% of your revenue is available to cover your fixed costs and contribute to profit. Watch this video from Investopedia reviewing the concept of contribution margin to learn more.
A business can increase its Contribution Margin Ratio by reducing the cost of goods sold, increasing the selling price of products, or finding ways to reduce fixed costs. A high Contribution Margin Ratio indicates that each sale produces more profit than it did before and that the business will have an easier time making up fixed costs. A low Contribution Margin Ratio, on the other hand, suggests that there may be difficulty in covering fixed costs and making profits due to lower margins on individual sales. As mentioned earlier, the contribution margin ratio can help businesses determine the lowest possible price at which sales can be made and still break even.
That said, most businesses operate with contribution margin ratios well below 100%. The contribution margin is computed by using a contribution income statement, a management accounting version of the income statement that has been reformatted to group together a business’s fixed and variable costs. The difference between leveraging process frameworks to simplify process the selling price and variable cost is a contribution, which may also be known as gross margin. The contribution margin measures how efficiently a company can produce products and maintain low levels of variable costs. It is considered a managerial ratio because companies rarely report margins to the public.
