
If actual cost exceeds standard cost, the resulting variances are unfavorable and vice versa. The overall labor variance could result from any combination of having paid laborers at rates equal to, above, or below standard rates, and using more or less direct labor hours than anticipated. Suppose a manufacturing company, ABC Ltd, sets a standard overhead rate of $10 per direct labor hour. The budgeted direct labor hours for a particular production run are 1,000 hours, resulting in an expected overhead cost of $10,000. However, during the production run, the actual overhead cost incurred amounts to $12,000.
Practice Video Problem 8-2: Computing direct labor variances LO3
This pipe is custom cut and welded into rails like that shown in the accompanying picture. If the resulting variance is positive, it signifies a favorable outcome, meaning the actual results exceeded expectations, such as lower costs or higher revenues. In contrast, if the variance is negative, it indicates an unfavorable outcome, implying that the actual results fell short of the forecasted amounts, such as higher costs or lower revenues. Thus a positive number is favorable and a negative number is unfavorable. In cost accounting, a standard is a benchmark or a “norm” used in measuring performance. In many organizations, standards are set for both the cost and quantity of materials, labor, and overhead needed to produce goods or provide services.
Sales Volume Variance: (Definition, Formula, Example, and Analysis)
The fixed component of manufacturing overhead is comprised of overhead costs that stay the same in total regardless of the quantity produced or another cost driver. For example, rent expense for the production factory is the same every month regardless of how many units are produced in the factory. Within the relevant range of production, fixed costs do not have a quantity standard, only a price standard. Fixed manufacturing overhead is analyzed by comparing the standard amount allowed to the actual amount incurred. Standards for variable manufacturing costs include both quantity and price standards.
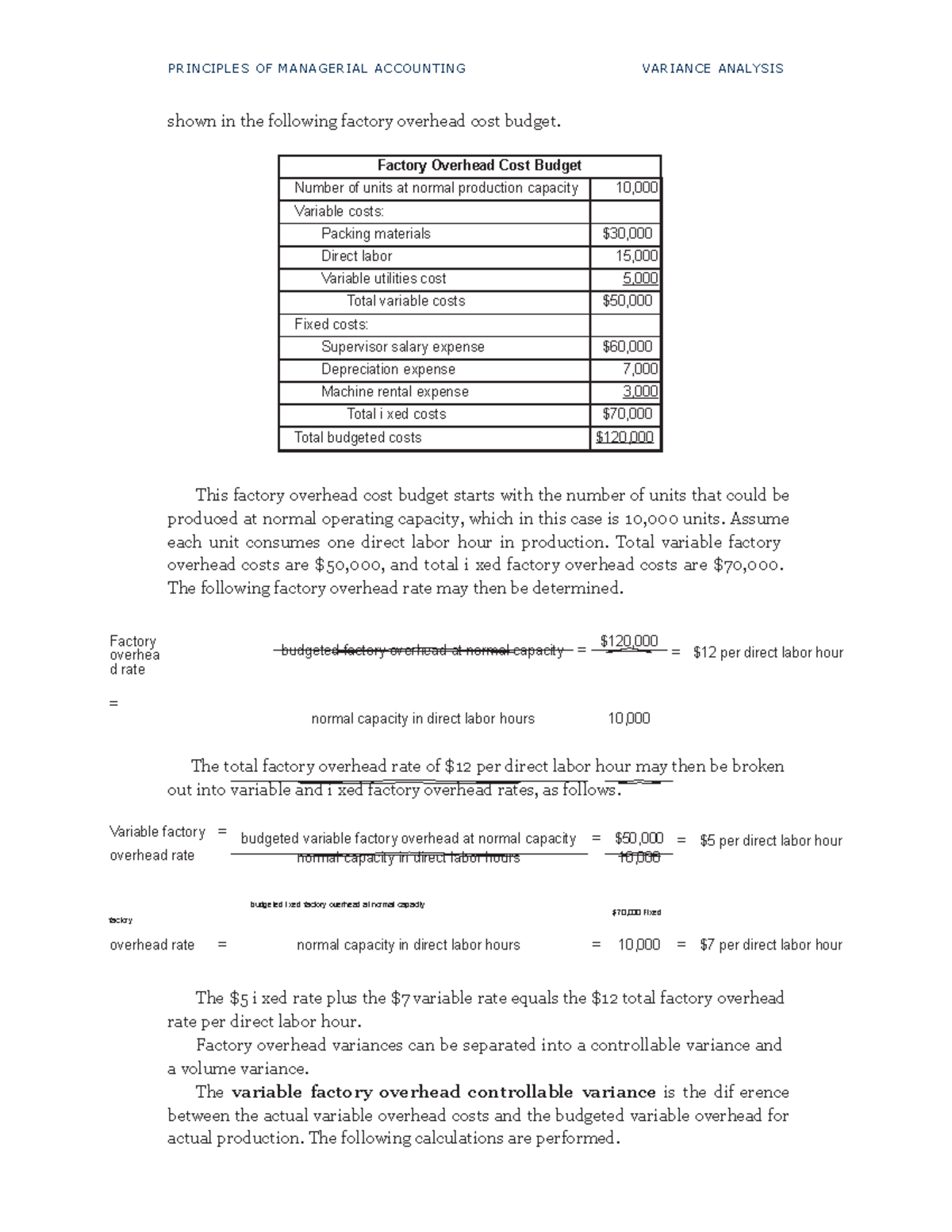
Explaining Differences in Expected and Actual Operational Outcomes
The sum of all variances gives a picture of the overall over-performance or under-performance for a particular reporting period. For each item, companies assess their favorability by comparing actual costs to standard costs in the industry. Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct materials variance template, compute the direct materials variances. Standard costs are established for all direct materials used in the manufacturing process. Direct materials include all materials that can be easily and economically traced to the production of a product. For example, the direct materials necessary to produce a wood desk might include wood and hardware.
Standard Costing Advantages Explained
Per the standard, total variable production costs should have been $1,102,500 (150,000 units x $7.35). However, Brad actually incurred $1,284,000 in variable manufacturing costs. Actual variable manufacturing costs transactions incurred were $181,500 over the budgeted or standard amount. The example of the NoTuggins dog harness is used throughout this chapter to illustrate standard costs and standard costs variances for product costs.
An unfavorable materials quantity variance occurred because the pounds of materials used were greater than the pounds expected to be used. This could occur if there were inefficiencies in production or the quality of the materials was such that more needed to be used to meet safety or other standards. An unfavorable materials price variance occurred because the actual cost of materials was greater than the expected or standard cost. This could occur if a higher-quality material was purchased or the suppliers raised their prices. Variance analysis facilitates performance measurement and control at the level of responsibility centers (e.g. a department, division, designation, etc). Therefore, the performance of each responsibility centre is measured and evaluated against budgetary standards with respect to only those areas which are within their direct control.
Brad decided to conduct a standard costs variance analysis to see if he could isolate the issue, or issues. The standard costs to make one unit of NoTuggins and the actual production costs data for the period are presented in Exhibit 8-1 below. Review the following graphic and notice that more is spent on actual variable factory overhead than is applied based on standard rates. This scenario produces unfavorable variances (also known as “underapplied overhead” since not all that is spent is applied to production). As monies are spent on overhead (wages, utilization of supplies, etc.), the cost (xx) is transferred to the Factory Overhead account.
The total direct labor variance can be calculated in the last line of the top section by subtracting the actual amounts from the standard amounts. The standard quantity allowed of 37,500 direct labor hours less the actual hours worked of 45,000 hours yields a variance of (7,500) direct labor hours. The total direct labor variance is the total standard labor costs allowed of $675,000 less the actual amount paid for direct labor of $832,500, which is $(157,500) unfavorable. The standard and actual amounts for direct materials quantities, prices, and totals are calculated in the top section of the direct materials variance template. All standard cost variances are calculated using the actual production quantity as the cost driver. At the highest level, standard costs variance analysis compares the standard costs and quantities projected with the amounts actually incurred.
- Standard cost projections are established for the variable and fixed components of manufacturing overhead.
- If the outcome is unfavorable (a positive outcome occurs in the calculation), this means the company was less efficient than what it had anticipated for variable overhead.
- During the period, Brad projected he should pay $675,000 for direct labor to produce 150,000 units.
- Direct labor is considered manufacturing labor costs that can be easily and economically traced to the production of the product.
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
An unfavorable labor quantity variance occurred because the actual hours worked to make the 10,000 units were greater than the expected hours to make that many units. This could occur because of inefficiencies of the workers, defects and errors that caused additional time reworking items, or the use of new workers who were less efficient. For instance, rent is usually subject to a lease agreement that is relatively certain. Even though budget and actual numbers may differ little in the aggregate, the underlying fixed overhead variances are nevertheless worthy of close inspection.
